About Me
I am a Master’s student at École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL), with a focus on computer vision and machine learning. I’m currently working as a research student focusing on parametrical diestortion-free Structure-from-Motion at CVG group under the supervision of Prof. Dr. Marc Pollefeys. Previously, I spent time in VITA lab working on pose-estimation based lane marker detection, supervised by Prof. Dr. Alexandre Alahi. Prior to joining EPFL, my deep-seated interest in human-centric technology led me to conduct research on the spread mechanisms of respiratory diseases at Zhejiang University, where I completed my bachelor’s degree, working under the supervision of Prof. Jianjian Wei.
Research Interests
My research interest primarily focuses on the application of deep learning to various computer vision tasks, such as image recognition, 3D localization, and 3D reconstruction. I am particularly interested in exploring these areas within the realm of autonomous vehicle perception. Additionally, I am keen to expand my expertise and gain practical experience in other domains including augmented reality.
Selected Projects
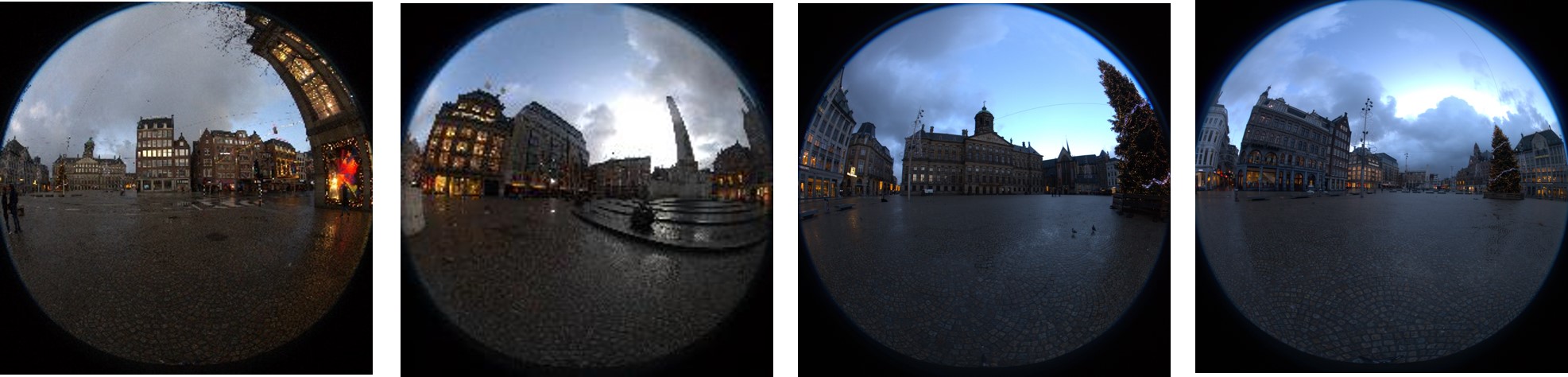
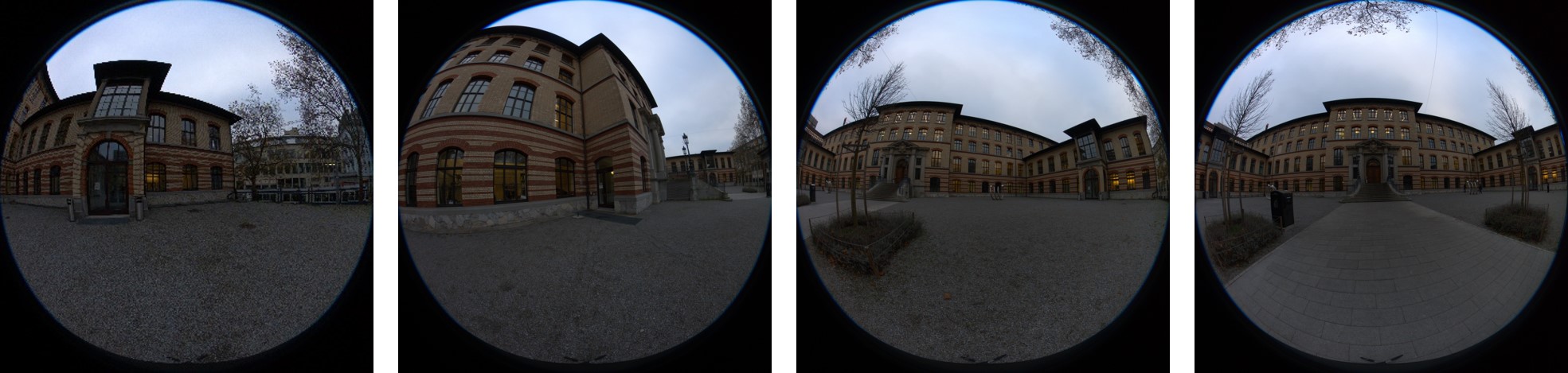
Beyond Structure-from-Motion with Camera Intrinsics
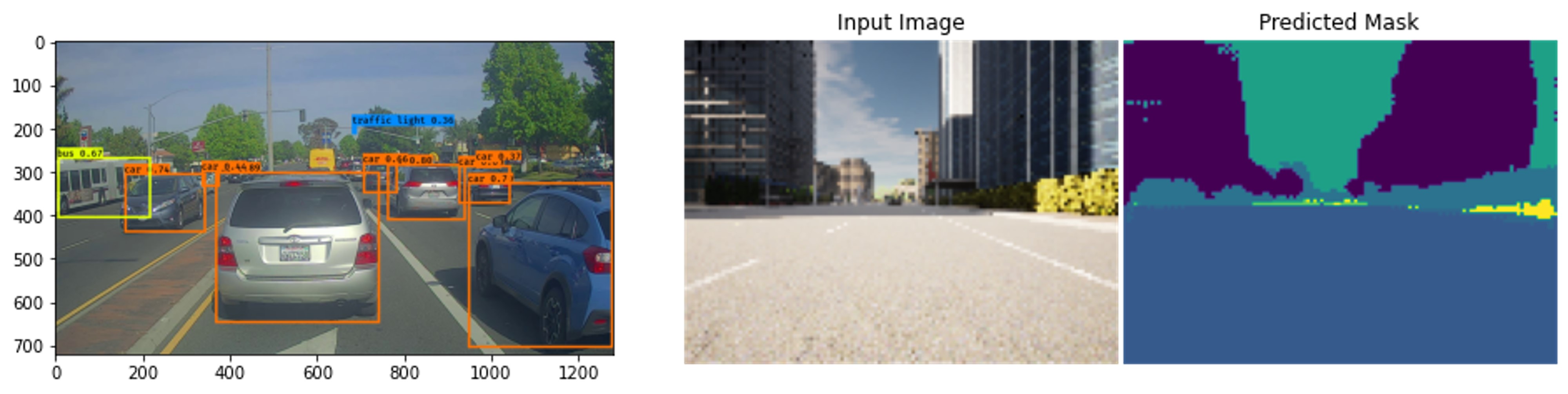
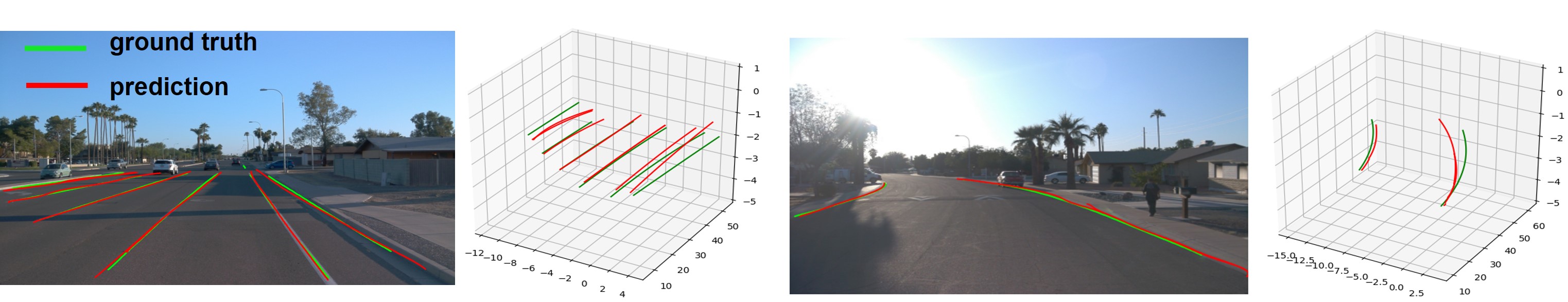
Pose Estimation Based Monocular 3D Lane Detection
Improving Neural Networks Performance with Zeroth-order and First-order Hybrid Optimization Methods
This project delves into the limitations of first-order (FO) gradient-based optimization in neural networks, exploring their gradient-free zeroth-order (ZO) alternatives like ZO-SGD and ZO-signSGD. Using a PyTorch-based framework, we implemented and compared ZO and FO methods across various network configurations and hyperparameters, assessing time efficiency, convergence rate, stability and overall performance for hand-written digits classification task. The study reveals ZO methods' increased stability and lower hyperparameter sensitivity, attributed to the regularizing effect of perturbation techniques in gradient estimation. However, ZO methods were found to be more reliant on model architecture and scaling. A hybrid FO-ZO approach emerged as a balanced solution, optimizing both gradient computation costs and efficiency.
Crafting a Personalized Beer Landscape: Analyzing User Preferences and Naming Impact for Guiding Targeted Recommendation
This project takes a deep dive into beer popularity and user taste preferences using review datasets from BeerAdvocate and RateBeer, consisting of both categorical ratings and textual reviews. Merging statistical methods with natural language processing techniques like sentiment analysis and word2vec, we uncovered a multi-faceted view of the beer domain, including the popularity of beer and the influence of naming on ratings, and the similarities between styles. Our findings provide tailored recommendations for users, considering not just popularity but also qualitative attributes and regional taste variations. An interactive webpage was also deployed, I invite you to click on the image and take a look at our data story.
Training a Chatbot for Commonsense Persona-grounded Dialogue Generation
We participated in the Commonsense Persona-grounded Dialogue Challenge organized by Sony and EPFL, which aims to generate dialogue responses that possess both persona consistency and contextual coherence. We enhanced a BART-based model by incorporating a knowledge-graph-based data augmentation technique and evaluated model performance given different set of augmentation settings and persona constraints. Our best-performing model achieved a word F1 score of 17.27, surpassing the baseline score of 17.001 set by GPT-3.5 Turbo using a simple prompt.
Deep Learning Specialization Projects
After initiating practical projects through the Deep Learning for Autonomous Vehicles @ EPFL, I opted for a structured learning path to thoroughly understand deep learning as it applies to computer vision by enrolling in the Deep Learning Specialization on Coursera. This program enabled me to acquire a robust theoretical foundation and hands-on experience in constructing efficient neural network architectures from the ground up—including ResNet, LSTM, Transformers, etc. Additionally, I applied these architectures to a range of computer vision tasks, such as vehicle detection using the YOLO framework and image segmentation utilizing the U-Net architecture.
Publications
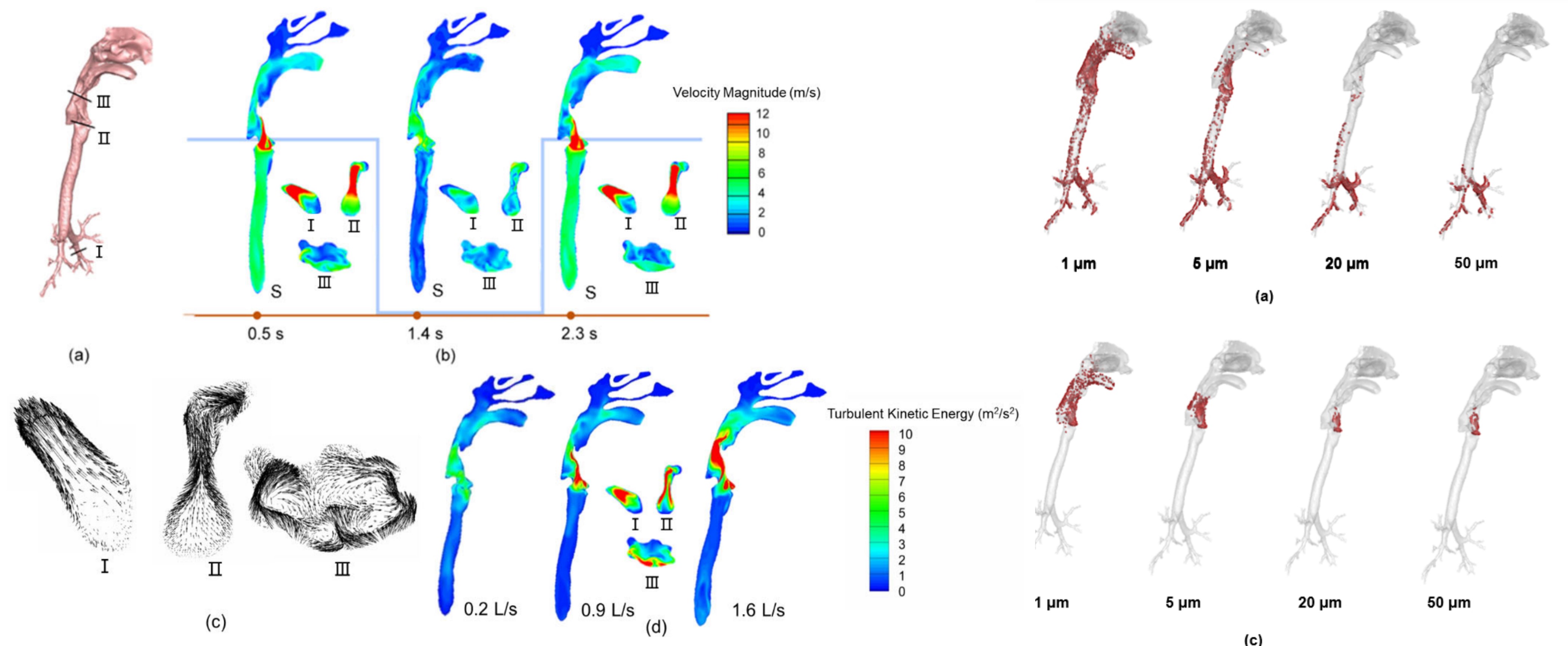
Tracing the origin of large respiratory droplets by their deposition characteristics inside the respiratory tract during speech
Yihan Wang, Jianjian Wei, Caroline X. Gao, Li Liu, Building Simulation, 16, 781 – 794 (2023), orally presented in IEHB (2021).
During the Covid-19 pandemic, the prevalence of asymptomatic and pre-symptomatic transmissions posed a continuous threat to public health, with the significance of airborne versus droplet-spray transmission being a subject of debate. To offer insights into non-pharmaceutical infection control measures, we carried out a computational fluid dynamics study to investigate the threshold at which differently-sized droplets, produced at primary SARS-CoV-2 replication sites, can escape during speech activities using a realistic human airway model. In conjunction with published medical data, our study emphasized the substantial risk posed by small droplets and highlighted the previously underestimated importance of the airborne transmission pathway.
Powered by Jekyll and Minimal Light theme.